Did you know that nearly 70% of your immune system resides in your gut? That’s right—your gut health plays a massive role in your overall well-being, and fermented foods are one of the easiest ways to support it! From tangy sauerkraut to creamy yogurt, fermented foods have been a staple in diets worldwide for centuries.
But what makes them so special? In this article, we’ll dive into the top benefits of fermented foods, backed by science, and explore how they can boost your gut health, improve digestion, and even enhance your mood.

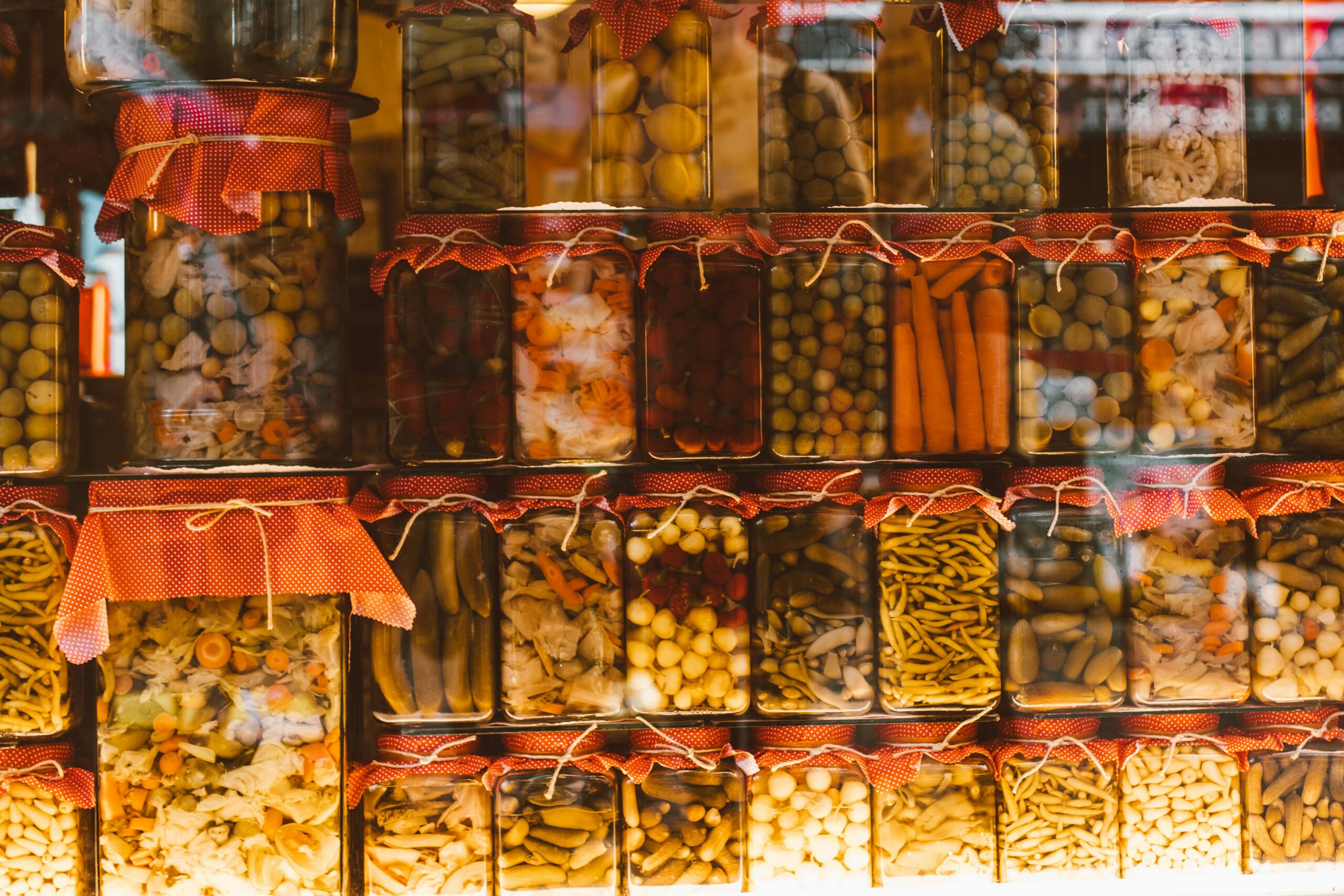
1.What Are Fermented Foods?
Definition of fermentation and how it works:
Fermentation is a spontaneous process that occurs when microorganisms, including yeast, fungi, or bacteria, convert carbohydrates (for example, sugars and starches) into acids or alcohols.
This is not exclusive to just food preparation, as fermentation occurs in the production of wine, beer, yogurt, and vinegar. This method not only aids in preserving food, but also gives it a lift in taste and nutritional value. It’s like Mother Nature decided to get extra creative with your meal!
Examples of popular fermented foods (e.g., kimchi, kefir, tempeh, miso, kombucha):
Fermented foods are as diverse as they are nutritious; from Korea’s tangy kimchi to the West’s fizzy kombucha. They all come in different flavors and forms. Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, miso, tempeh, and even sourdough bread are all types of fermented foods that can be found in different parts of the globe.
Brief history of fermentation in different cultures:
Fermentation is certainly not a new ‘trend’ only discovered recently. It goes back thousands of years. Ancient civilizations once used fermentation as a method to preserve food due to the lack of fridges.
For example, kimchi has been in Korean food for over 2,000 years while helping sauerkraut in extending sailor’s lifespans during long journeys by preventing scurvy.
2. Enhancing Digestion and Gut Health
How helpful probiotics are introduced to the gut through fermented foods:
Fermented foods contain live probiotics which are good bacteria that help your gut. The beneficial probiotics maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms in your digestive system, leading to better digestion and nutrient absorption.
The role of probiotics in balancing gut microbiota:
Your gut is packed with trillions of bacteria, each with positive and negative attributes. The probiotics in fermented foods enable the good bacteria to thrive dominantly creating a balanced gut microbiome. Such balance is crucial to prevent digestive issues such as irregular bowel movements, gas, and bloating.
Minimizing the symptoms of IBS, constipation, and bloating:
Kefir is a type of fermented food that has been linked with lessened bloating and better stool consistency in people suffering from IBS. Other studies also indicate that probiotics within fermented foods are capable of alleviating the symptoms for IBS and other forms of digestive disorders.
3. Enhanced Immune System
Relationship between gut health and immune response:
Almost seven out of ten people do not know that their immune system lies mostly within their abdomen. The fermented foods help heal your gut in turn giving you a strong immune response for protection against severe diseases.
How fermented foods fortify the gut barrier:
Consumption of fermented foods helps in the production of specific proteins known as tight junction proteins; they work like a fence against toxins and bad bacteria. This is called the prevention of “leaky gut” and is important for immunity.
The studies outlined show lower rates of infections from repeated consumption:
People who consumed fermented foods regularly had fewer cases of respiratory infections, and if they did fall sick, they recovered much faster. For example, a study published in Frontiers in Microbiology stated that probiotics in fermented foods help lessen the intensity and frequency of colds and flus.
4. Improved Nutrient Absorption

Fermentation boosts bioavailability of nutrients such as B vitamins and iron:
Fermentation is a process that simplifies nutrients making them easier for the body to digest and absorb. For example, fermented dairy products like yogurt increase the bioavailability of B vitamins which are crucial for energy production in the body.
Break down of anti-nutrients for easier digestion (e.g., phytic acid):
Phytic acid is one example of an anti-nutrient that can inhibit the absorption of minerals such as iron and zinc. With fermentation, these anti-nutrients are nullified resulting in the food being packed with nutritious goodness.
Nutrient-rich fermented foods include the following:
While tempeh boasts protein and iron, miso is packed with vitamin K and antioxidants. Sauerkraut, however, is even better due to its vitamin C and fiber content!
5. Supporter of Mental Health and Mood

Fermented foods, probiotics, and mental health- how is it connected?
The gut and brain are constantly communicating via the gut-brain axis. It is important for everyone to understand how a healthy gut can positively impact gut microbiome. A healthy gut can produce ‘feel-good’ hormones such as serotonin which has a critical role in mood regulation.
Probiotics and complemented medicine approach: alleviating anxiety and depression symptoms
Research proves that probiotics found in fermented foods can lessen depression and anxiety symptoms. Take for instance, the 2017 research carried out on a group of people who ate fermented foods. The results showed lower levels of social anxiety.
Research focused on fermented foods showed positive results on mood and cognitive functioning.
Kefir and kimchi have been associated with improved brain functioning and reduction in brain fog. Good news is that having a healthy gut reduces inflammation which is often associated with mental health problems.
6. Managing Weight and Metabolism

The benefits of fermented foods for achieving healthy weight loss:
Like many wonder foods, fermented foods are low in calories and nutrient rich, making them easy to incorporate into any weight-loss plan. Probiotics aids in appetite control and softens the desire for consuming unhealthy, sugary food.
How probiotics help with controlling appetite and decreasing fat retention:
Some important strains of probiotics, such as Lactobacillus gasseri, is known to reduce belly fat while preventing weight gain. The work by regulating the hormones responsible for people’s hunger and the body’s fat retention.
Low-calorie, nutrient-dense fermented foods:
Kombucha, kimchi and sauerkraut are low calorie but full of taste and nutrition. You can use them to spice up your meals without worrying about adding additional calories.
7. Reduction of inflammation and the risk of chronic diseases

The anti-inflammatory characteristics of fermented foods:
Fermented foods are one of the best solutions for many people with chronic inflammation since they possess roots of many diseases, as they are filled with antioxidants and anti-inflammatory foods, and compounds fermented food aid in incorporating inflammation.
How probiotics fight oxidative stress:
Brought out by fermenting foods, probiotics help eliminate free radicals that cause oxidative stress, which lowers the risk of chronic diseases and conditions, such as heart problems and diabetes.
Head to healthful fermented foods that may aid heart health, diabetes, and autoimmune conditions:
The consumed fermented foods seem to actively participate in cholesterol control, blood sugar regulation, and even alleviating symptoms in autoimmune diseases’ patients. For example, rheumatoid arthritis has shown symptom improvements among participants.
8. Improved health in the skin.

Probiotics and inflammation of skin conditions:
Skin is directly related to gut health. Gut microbiome is known to downsize inflammation, which is linked to skin issues like eczema, and acne.
Fermented foods for acne, eczema, and rosacea treatment:
Skin microbiome can be balanced by fermented foods’ probiotics leading to less breakouts and better skin texture. Kefir, for instance, has been shown in studies to lower the severity of acne.
Examples of collagen rich fermented foods:
Miso and tempeh are fermented foods that are rich in amino acids and aid collagen production thus keeping the skin young and firm.
9. Easy to Incorporate into Your Diet

Ways to add fermented foods into meals is easy.
You can add sauerkraut to sandwiches, mix kimchi into rice bowls or have some kombucha with your meal. The list is endless!
DIY fermentation tips for beginners:
Begin with easier ones such as homemade sauerkraut or yogurt. All you need are fresh vegetables, some salt, and a jar.
Store bought vs homemade fermented foods: what to look for:
While buying fermented foods at the store, look for labels saying “live and active cultures” if you want to take advantage of the probiotics.
10. Potential Side Effects and Considerations

Who should avoid fermented foods: people intolerant to histamine sufferings.
People with histamine intolerance or certain digestive conditions such as SIBO will perhaps need to avoid fermented foods as they often may aggravate symptoms.
Ways to introduce fermented foods: incrementally, to minimize digestive discomfort.
Take small portions to start with and then gradually increase to allow your gut to cope with the change.
Balancing fermented food with the rest of diet.
Besides being helpful, fermented foods should be included in a balanced diet with different whole foods.


